bf-workflows
Git
What is Git?
Git is the most popular version control system, widely used for tracking changes in source code during software development.
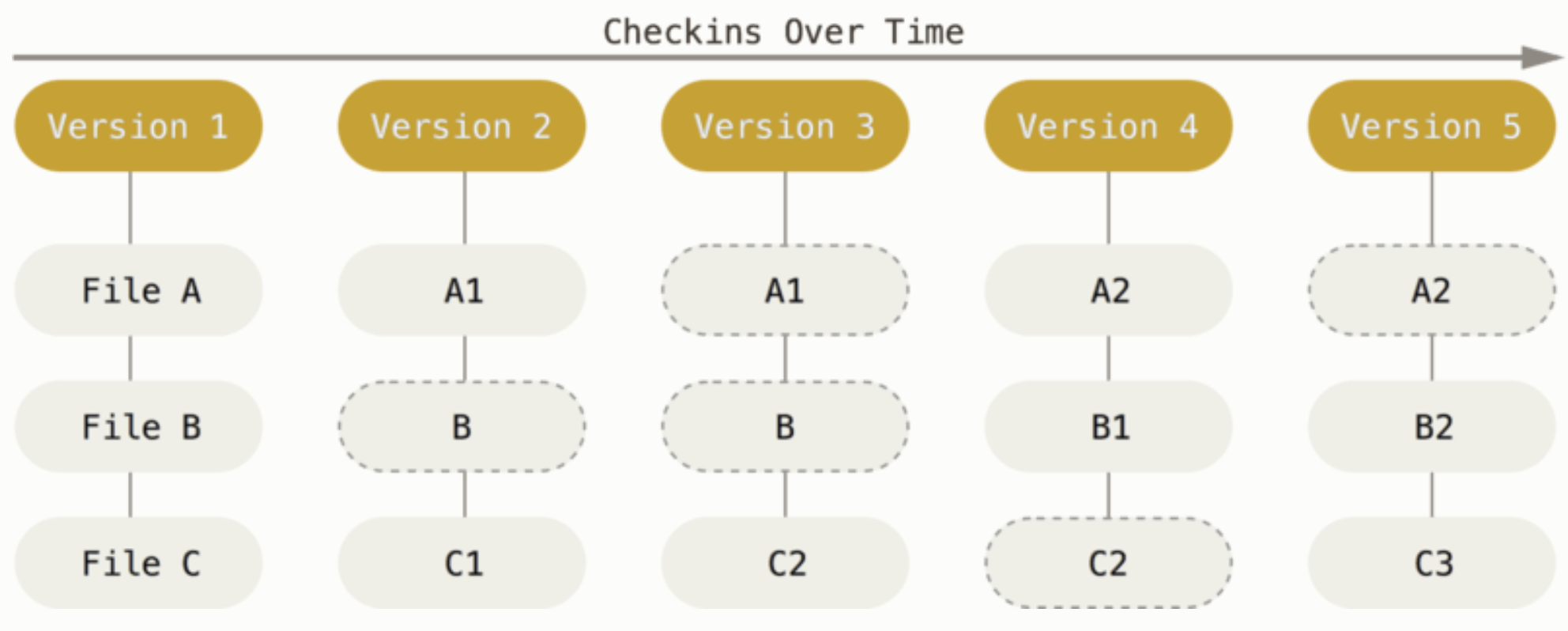
Key Features of Git
- Local Storage: Git is software that runs locally on your computer. Your files and their history are stored on your machine.
- Change Tracking: Git tracks the changes you make to files, allowing you to see a history of modifications.
- Collaboration: Git simplifies collaboration by enabling multiple developers to merge their changes into one source.
Git Repositories
A Git repository is a hidden subfolder within your project directory that contains all of your project files and the entire revision history.
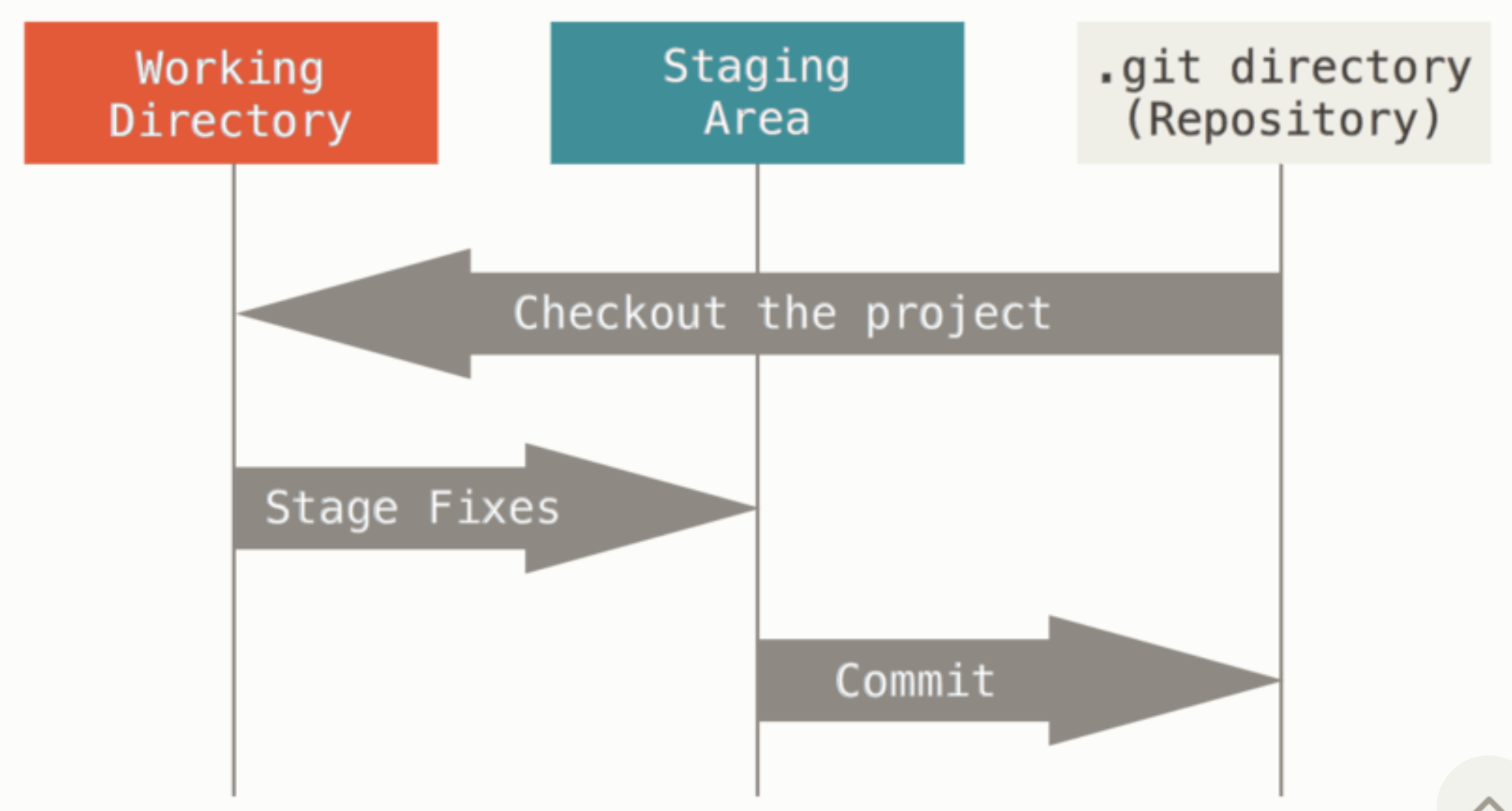
The Three States of Git
Git files can reside in one of three states: modified, staged, and committed.
- Modified: Changes have been made to the file(s) but not yet committed.
- Staged: Changes have been added to the staging area and are ready to be committed.
- Committed: Changes have been committed and saved to the local repository.
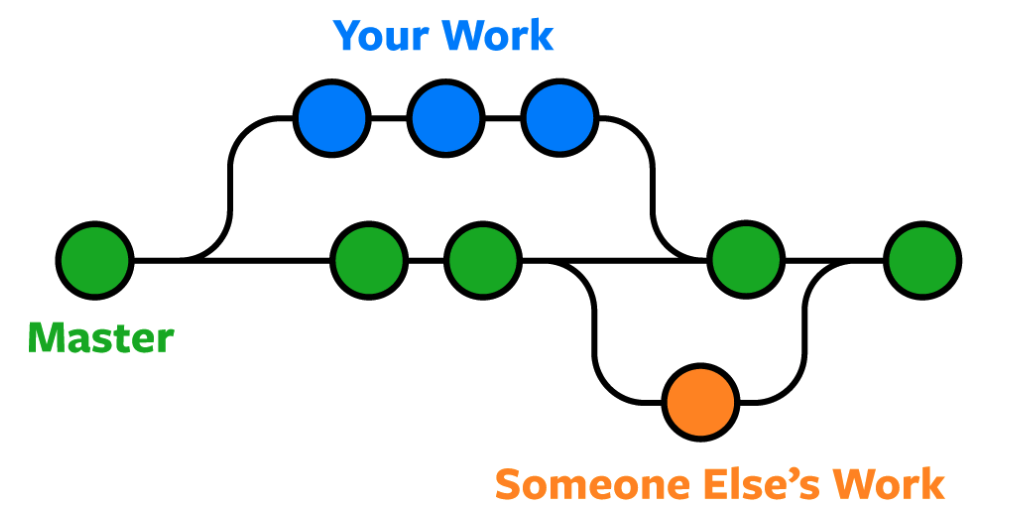
Git Branching
Git allows you to create branches, enabling you to work on different features or
fixes without affecting the main branch. This facilitates parallel development
by multiple developers.
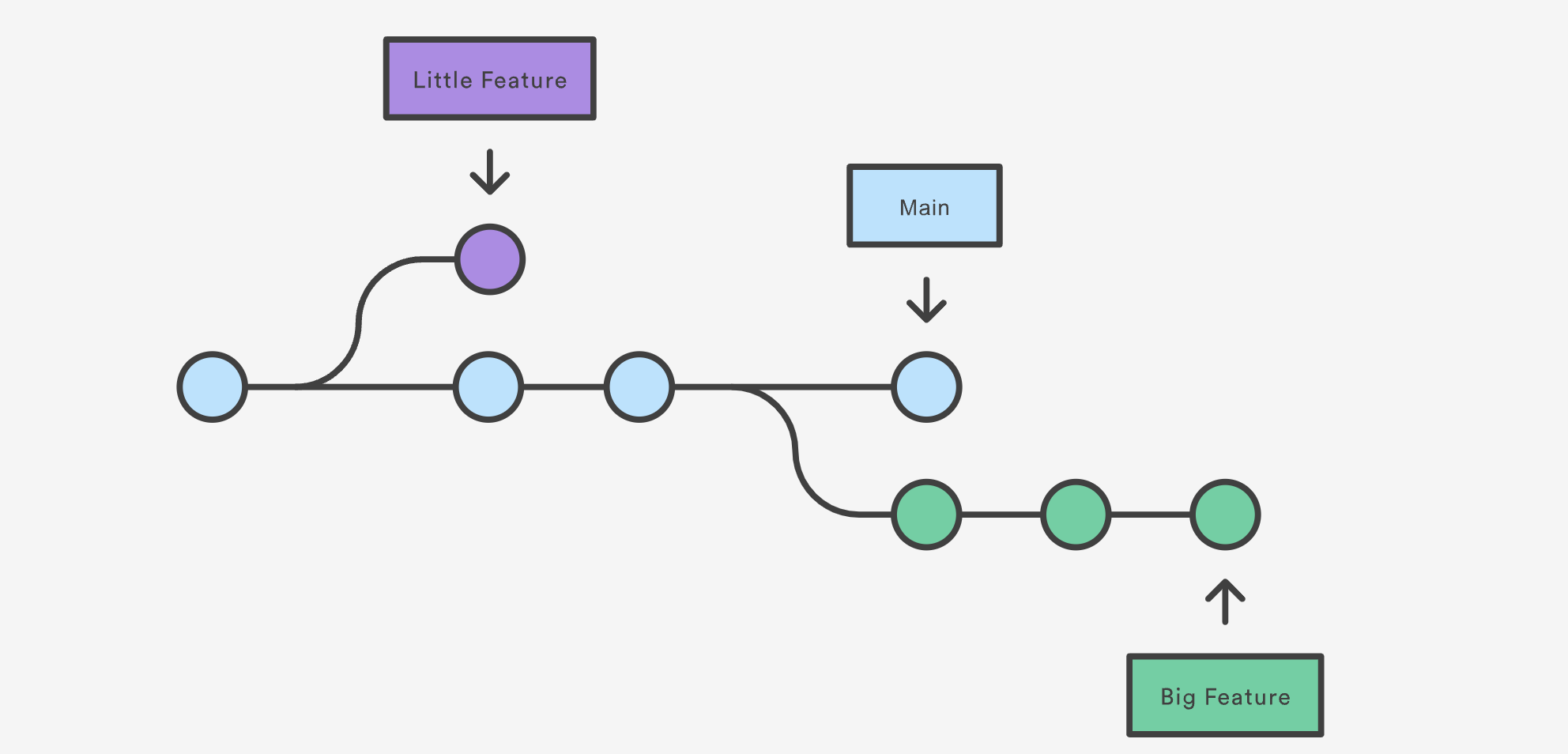
Git Merging
Git merge combines two separate development histories into one. For
instance, you can merge changes from a feature branch into the main branch to
integrate new features or bug fixes.
Common Git Commands
Configuring Git
Set your Git username:
git config --global user.name "Your GitHub Username"
Set your Git email:
git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
Set VS Code as the default editor:
git config --global core.editor "code --wait"
Handle end-of-line configurations:
-
For macOS or Linux:
git config --global core.autocrlf input -
For Windows:
git config --global core.autocrlf true
View all global configurations in VS Code:
git config --global -e
Initializing and Checking Status
Initialize an empty Git repository:
git init
List all untracked files:
git status
Staging and Committing Changes
Add a file to the staging area:
git add <file-name>
Add all files to the staging area:
git add .
Remove a file from the staging area:
git reset <file-name>
Commit changes with a descriptive message:
git commit -m "Descriptive message"
Stashing Changes
Save changes temporarily without committing them:
git stash
Restore stashed changes:
git stash apply
Branching and Merging
Create a new branch:
git branch <branch-name>
Switch to a new branch:
git checkout <branch-name>
Create a new branch and switch to it:
git checkout -b <branch-name>
Reverting and Resetting
Revert a commit:
git revert <commit-hash>
Reset changes:
git reset
Viewing History and Differences
Display the most recent commits:
git log
Compare changes between commits:
git diff
Rebase
Integrate changes from one branch onto another:
git rebase <branch-name>