html-css-reference
HTML
What is HTML ?
- HTML stands for
Hyper Text Markup Language - HTML is the standard
markup languagefor creatingWeb pages - HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a
series of elements - HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as “this is a heading”, “this is a paragraph”, “this is a link”, etc.
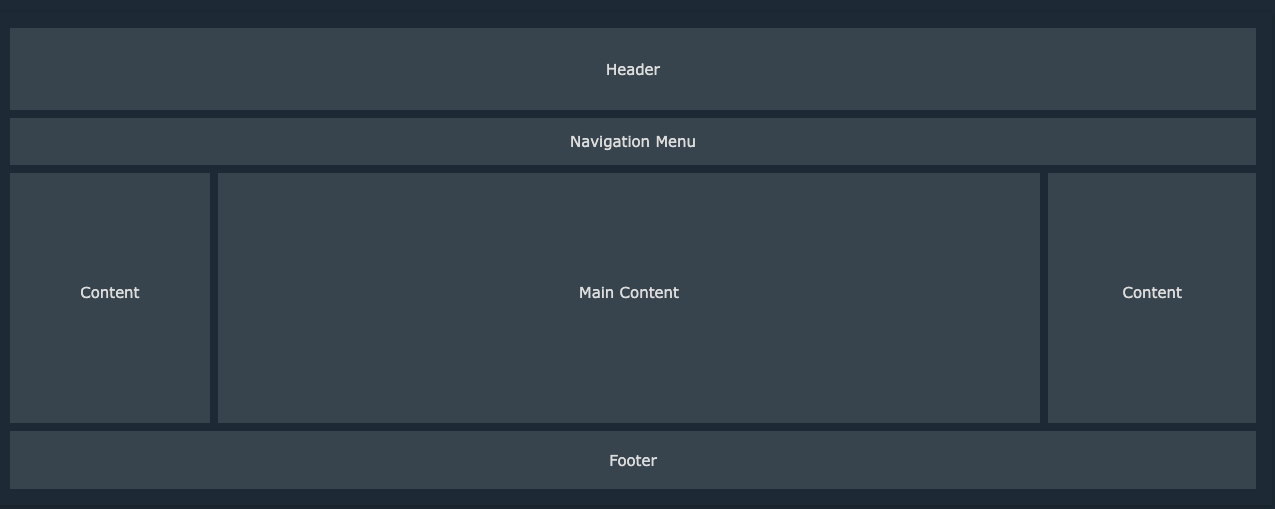
HTML structure
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- TODO: Write your comments here -->
<link rel="icon" href="http://example.com/favicon.png" />
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
</header>
<main>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</main>
</body>
</html>
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document - The
<html>element is the root element of an HTML page - The
<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page - The
<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab) - The
<body>element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings,
HTML element
An HTML element is defined by a open <tag>, some content and close </tag>.
Note: Some HTML elements have no content (like the <br> element). These
elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag!
Headings
<h1>This is heading 1</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6</h6>
Paragraphs
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
Links
<a href="https://hackyourfuture.be/">This is a link</a>
Images
<img src="hyf.jpg" alt="hyf" />
Attributes
All HTML elements can have attributes Attributes
provide additional information about elements Attributes are always specified
in the start tag Attributes usually come in name/value pairs like:
name="value"
Formatting elements
<b>- Bold text<strong>- Important text<i>- Italic text<em>- Emphasized text<mark>- Marked text<small>- Smaller text<del>- Deleted text<ins>-Inserted text<sub>- Subscript text<sup>- Superscript text
Tables
<table>
<tr>
<th>Company</th>
<th>Contact</th>
<th>Country</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Alfreds Futterkiste</td>
<td>Maria Anders</td>
<td>Germany</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Centro comercial Moctezuma</td>
<td>Francisco Chang</td>
<td>Mexico</td>
</tr>
</table>
Lists
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ol>
Block and Inline Elements
Block-level Elements
A block-level element always starts on a new line, and the browsers automatically add some space (a margin) before and after the element.
Inline Elements
An inline element does not start on a new line.
<p>Hello World</p>
<div>Hello World</div>
<span>Hello World</span>
Iframe
An inline frame is used to embed another document within the current HTML document.
<iframe
src="demo_iframe.htm"
height="200"
width="300"
title="Iframe Example"
></iframe>
Responsive Web Design
A responsive web design will automatically adjust for different screen sizes and viewport.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
Semantic Elements
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
Examples of non-semantic elements: <div> and <span> - Tells nothing about
its content.
Examples of semantic elements: <form>, <table>, and <article> - Clearly
defines its content.
Absolute path vs relative path
<img src="https://www.w3schools.com/images/picture.jpg" alt="Mountain" />
<img src="../assets/html-css.png" alt="Mountain" />
Entities
<!-- copyright -->
<div>©</div>
Symbols
<!-- euro -->
<div>€</div>
Emojis
<!-- smiley face -->
<div>😀</div>
Forms
<form>
<label for="firstName">First name:</label><br />
<input type="text" id="firstName" name="firstName" /><br />
<label for="lastName">Last name:</label><br />
<input type="text" id="lastName" name="lastName" />
</form>
<!--
<input type="button" />
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="color" />
<input type="date" />
<input type="email" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="month" />
<input type="number" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="range" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="search" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="tel" />
<input type="text" />
<input type="time" />
<input type="url" />
<input type="week" />
-->
Videos
<video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
</video>
<audio>
<source src="horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg" />
</audio>